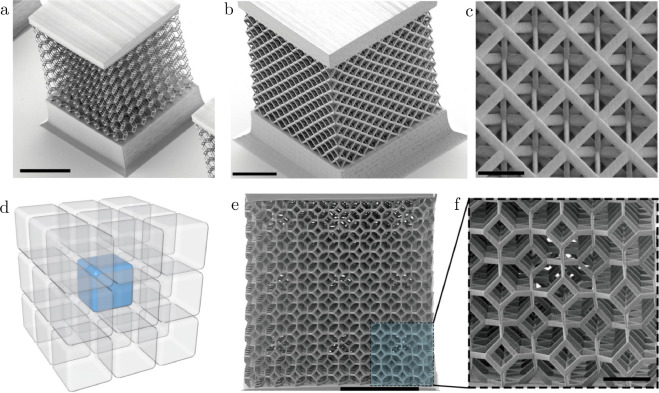
Recent advances in additive manufacturing at small scales has revealed the exceptional mechanical properties that can be achieved by truss-lattice materials. This study investigates the response of four topologically distinct truss-lattice architectures to the inclusion of defects in order to elucidate how defects influence the elastic properties of these materials. Numerical results from finite element models of periodic beam networks with missing building blocks are compared to both analytical continuum models with a micromechanical basis and to experiments with characteristic feature sizes on the nano and micro scales. Notably, this comparison reveals that the elastic properties of highly connected lattice-truss materials respond to defects in the same manner as homogeneous materials.
Click here to go to article